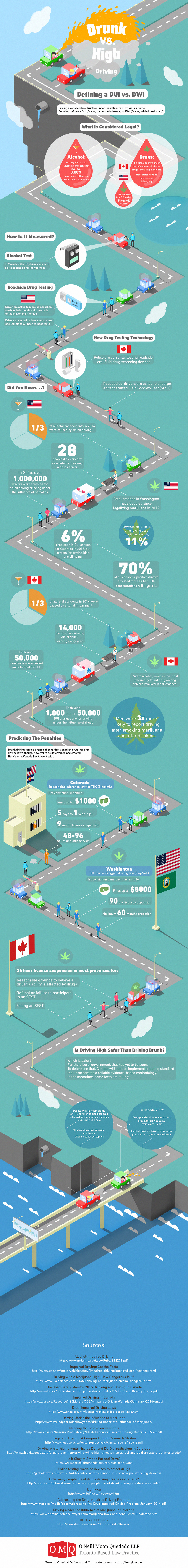
Marijuana and alcohol are two widely used substances that can be harmful. Despite this, both are readily, if not legally, available to individuals of all ages, a fact that largely contributes to the way in which both are socially accepted.
Socially, people associate getting high and being tipsy with having a good time. It’s easy for someone to take a sip from a friend’s drink or smoke a joint being passed around. However, most aren’t aware of the extent to which their brain is affected when they do so.
The legalization of marijuana, in particular, is a hot topic right now, especially with Canada being next in line to legalize the drug recreationally in 2017. Consequently, there’s a lot of discussion around the “marijuana vs. alcohol” topic that’s helping to put the substance into perspective to create a feasible legal framework.
In other words, can Canada draft up appropriate laws to reflect and take into account the severity of the impact of both substances? How will it be reflected in laws that relate to driving, for instance?
Here’s a brief look at how marijuana and alcohol impact the brain.
The Cognitive Impact Of Alcohol And Marijuana Consumption
Without doubt, smoking marijuana comes with major cognitive side effects. The psychoactive constituent tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in marijuana is what affects you. It attaches to the cannabinoid receptors in your system which interferes with the natural communication of cannabinoids between the neurons. These cannabinoid receptors are more dense in certain parts of the brain like the cerebral cortex which play a factor in how your memory, thinking, and consciousness are affected. This is why it can impair your concentration and affect how information is processed. Thus, while users may think smoking marijuana is harmless and has no lasting effects, the effects on your brain are immediate and can affect your safety.
Similarly, the negative effects of alcohol on the brain can never be overestimated. Although it’s known that the effects of alcohol depend upon factors such as age, the amount of alcohol consumed, size and so on, the impact of alcohol on different parts of the brain can be seen. When the Cerebral Cortex is affected, you feel less inhibited as information processing is slowed, and when it affects the medulla, your automated functions like breathing and consciousness are affected, making you feel sleepy. These are all indications of alcohol impairment.
Impacts of Marijuana And Alcohol Addiction
Also complicated is the topic of addiction, but one that shouldn’t be ignored. It’s been argued that as a soft drug, marijuana doesn’t cause any of the addiction or damage that is caused by other, “hard drugs” such as cocaine and heroin. However, it’s possible to undergo a use disorder experience in which you become dependent on marijuana without being addicted to it, only giving you the withdrawal symptoms of an addition. According to the National Institute of Drug Abuse, dependence on marijuana “occurs when the brain adapts to large amounts of the drug by reducing production of and sensitivity to its own endocannabinoid neurotransmitters.” Thus, just with regular marijuana use alone, you may be conditioning your brain into an addiction-like state.
With alcohol, the addiction can be both emotional and chemical. Alcohol is a depressant, but it also increases the release of dopamine. People turn to alcohol because makes them feel good, but what it’s also doing is impacting the brain and how the frontal cortex controls the amygdala, which controls emotions like depression. The addiction starts when the dopamine effect decreases and people have to keep drinking to get the same dopamine effect. The impact alcohol has, as anyone with a loved one suffering from alcoholism can attest, goes beyond the chemical, making it a highly personal issue as well.
The Long Term Impacts Of Marijuana And Alcohol
Moreover, long term alcohol consumption (or regular binge drinking over a short period) can actually physically change your brain structure. Over time, gray-matter cells that are responsible for memory, learning and making decisions have been shown to shrink in brain scan images. Connective white matter cells also get damaged, as well. Long term alcohol dependence can result in thiamine deficiency which can develop serious brain disorders (such as Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome) and liver dysfunction. The latter has the double effect of impacting the production and supply of nutrients to the brain and the filtration of harmful substances that can damage the brain. Clearly, long term drinking is nothing to take lightly. The longer one drinks, the worse the damage gets.
Likewise, long-term marijuana usage is said to have an impact on the brain, and in particular, for younger users. It has been shown in studies that during the adolescent stage the brain is still developing and forming synaptic connections. The endocannabinoid system is known to be involved in forming the proper connections between neurons (synapses). The THC in marijuana affects this development. Thus, smoking marijuana heavily during your adolescent years is shown to play a significant role in intelligence levels, lowering IQ scores during examinations.
Drinking Alcohol vs. Smoking Marijuana
While the debate on which substance is worse continues, it’s clear that each has its own negative and lasting impacts on the brain. Combining alcohol or marijuana with daily activities can be a lethal combination where alertness and judgement are needed, especially when it comes to certain activities like driving. In fact, now that marijuana is being legalized in Canada, the effects of drinking and driving versus driving while high are being closely looked at.
As this one infographic by OMQ Law shows, for instance, a person with 13 micrograms of THC per liter of blood are said to be just as impaired as someone with a BAC level of 0.08%. This is an interesting fact when you try to determine at what point a marijuana smoker is cognitively impaired, which can be complicated in itself as all people differ.
Here’s a closer look at how the effects listed above connect and relate to alcohol and marijuana driving laws in both US and Canada.